How to Pass Microsoft Azure AZ-900 Exam in 3 days
AZ-900 is the exam that test on foundation level knowledge of cloud concepts and Azure services.
Microsoft Azure AZ-900 is the exam that test on foundation level knowledge of cloud concepts and Azure services. Those who have experiences in other major cloud providers might find the most of AZ-900 materials to be very similar to they have learned.
I found the content of this exam to be very beneficial for anyone who would like to break in cloud computing on Azure.
Also Read: What is Microsoft Azure cloud computing?
This exam guide will give you all the information you need to pass the exam in 3 days or less.
Information about this exam
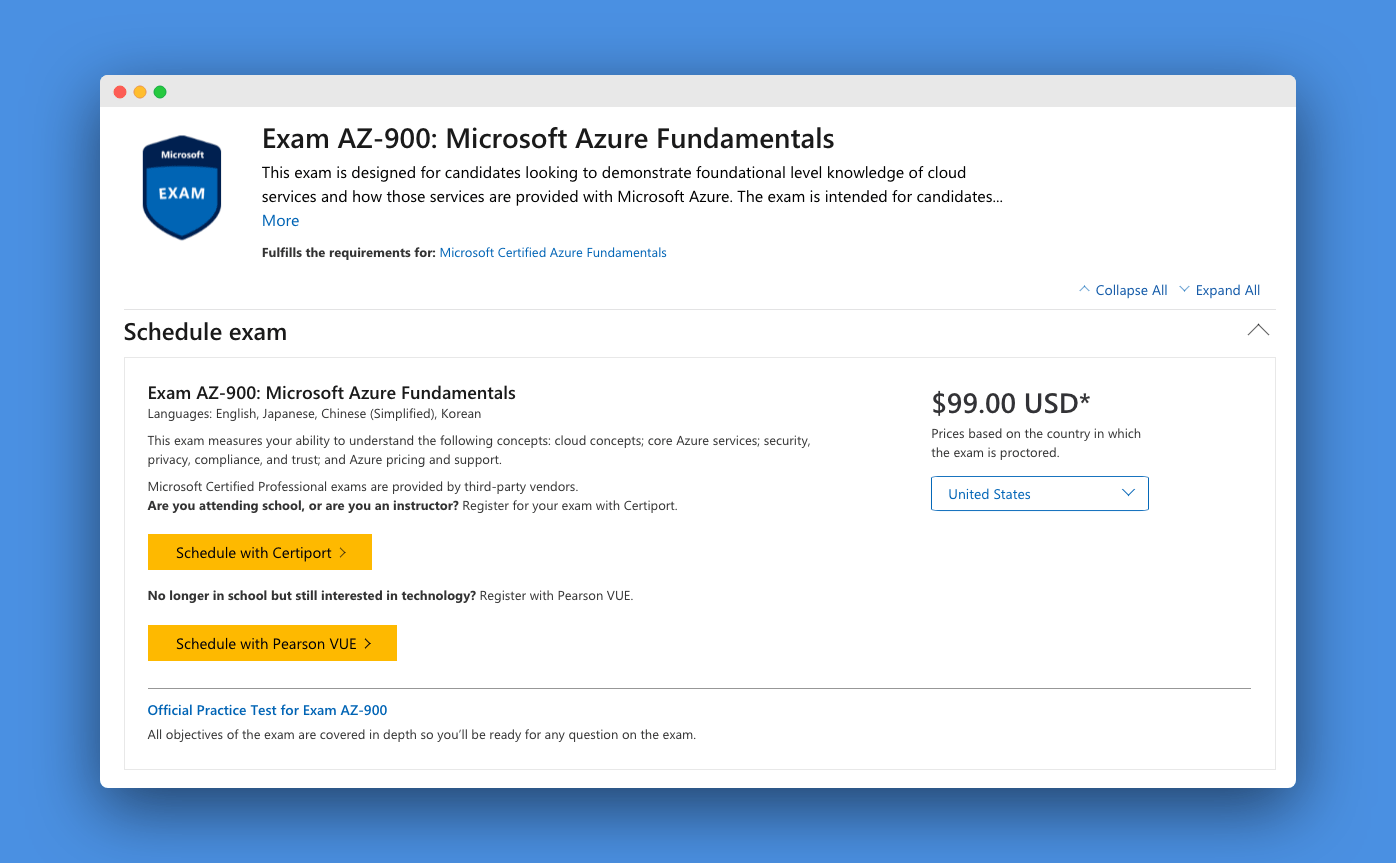
Most of the exam information is on Microsoft website. However, before going into the exam, I was researching how long is this exam. The Microsoft website does not show how many questions and how long the exam is.
So I gathered these numbers based on my exam:
- Questions: 44 (40–60 questions based on Whizlabs)
- Duration: 1 hour (85 minutes based on Whizlabs)
What I like about this exam is: Your result sheet is printed right after the exam, so you can see which area you are doing well and which area you need to work on.
This is the same study plan I used to pass AZ-900 exam:
- 2 day for learning from Microsoft Learn Platform
- 1–1.5 day for exam preparation
One day means 6–8 hours of work. So it might take around a week to study 2–3 hours per day after work.
Resources I used for studying AZ-900
I studied from 3 resources and spent around $15 for the preparation (excluding $99 for AZ-900 exam itself).
The 3 resources are:
[Free] Microsoft Learn platform (11 modules)
Microsoft provides a free learning platform for everything you need to pass any Azure certificate.
Unlike other learning platforms such as Google Cloud’s Coursera or Udemy, Microsoft Learn platform is 90% text with few short videos here and there. However, the material is great quality and the learning platform is easy to use.
I found that by having learning material in text, I can take note much faster by copy-paste the text directly.
This course took me 9–10 hours including taking notes and research on random technical words e.g. N-tier architecture.
[$15] Udemy course “Microsoft Azure Beginners Guide”
This Udemy video course contains all you need to know to pass AZ-900 exam. The content is more hands-on than Microsoft Learn since you will see the instructor showing you inside Azure Portal, whereas Microsoft Learn only teach you in text.
The beginners in Azure will learn a lot more from seeing real Azure portal than reading.
For me, I had some experience playing around Azure portal before. So I skipped to the last section: AZ-900 Preparation. This section provides 70 questions x 2 practice tests.
I found the practice questions to be very similar to Whizlabs, the last resource I used for exam preparation. I have heard from my colleague who passed AZ-900 only using this course.
My recommendation is you could study from videos in this course or from Microsoft Learn. The content should be very similar.
At my company Servian, we provide Udemy Business subscription for staffs. So I can access this course for free.
[$15] Whizlabs AZ-900 Exam Practices Tests
Whizlabs is the popular website containing a lot of IT exam practice tests. Note that Microsoft also offers Official Practice Test but at the significantly higher cost and a similar number of practice questions. So I went for Whizlabs this time.
Also Read: What is Microsoft Azure cloud services?
At the time of writing, Whizlabs has 3 practice tests with 55 questions each. The questions are surprisingly similar to the real exam, so you can get a feeling of what kind of questions you would get examined on.
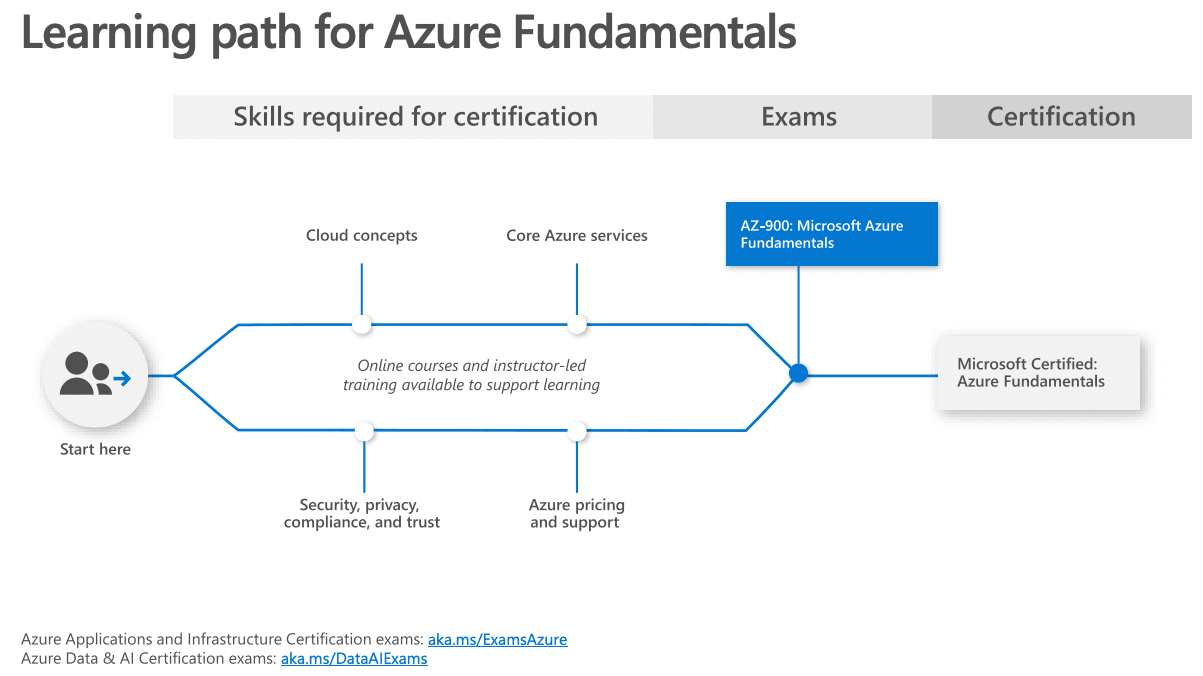
AZ-900 Exam Content
This section is based on the list from Microsoft website which is quite accurate to the exam.
There are 4 main parts. For each part, I am giving summarized information here to speed up your learning or you can also use them as revision material.
Part 1) Cloud Concept
This part contains general knowledge about cloud computing e.g. what are the benefits of cloud, the differences types of cloud service offering, and the differences in cloud deployment models.
Technological benefits of cloud:
- High Availability — The major cloud providers (Azure, AWS, GCP) have multiple data centers spread around throughout the world. Data and code stored in the cloud are copied to more than one data center. If anything happens to one data center, the data can be recovered from another data center.
- Fault Tolerance — In case there is any fault in the application or infrastructure, the service can continue to work by moving the work to other healthy servers.
- Disaster Discover — The data in the cloud can also get copied to other regions e.g. copy data from West US to East US. If there is natural disaster happened in West US and every data center goes down, the data center in East US will still have the copy of data.
- Scalability — The application running in the cloud can expand its size when there are more users in the system.
- Elasticity — The application running in the cloud can shrink its size when there are fewer users in the system. The users can also set automatic shutdown during the non-business hours to save money.
Business benefits of cloud:
- Agility — Cloud allows the business to deliver IT system to customers faster. The machines in the cloud are ready for cloud users to spin up when they need and shut down when they are not required.
- Economies of scale — Cloud is a shared pool of machines and services. As the number of customer grows, the cloud providers can lower the cost or increase quality of the services.
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx) vs Operational Expenditure (OpEx) — Building a data center requires large capital investment for hardware as well as the facility. A data center will also require ongoing electricity and staffs cost for operation. By using cloud, the capital expenditure for building a data center is not required.
- Consumption-based model (pay-as-you-go) — The cloud users only pay for what they need, by the duration they need.
Types of cloud service offering:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) — In this offering, the cloud providers offer barebone hardware in managed data center such as virtual machine or file storage. The cloud providers will take care of the physical infrastructure e.g. data center security or hardware repair, while the cloud users need to take care of server maintenance. For example, Azure VM allows the users to spin up new virtual machines in any size.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service) — The cloud providers will take care of the servers. The cloud users only need to bring in application code or data. For example, Azure SQL Database is fully managed service by Azure that the users do not need to / cannot access anything beyond their data.
- SaaS (Software as a Service) — The cloud providers will take care of both servers and code. The cloud users only need to configure the software to suit their needs. For example, Office 365 allows the users to use Microsoft Office software suite.
Differences in cloud deployment model:
- Public Cloud — When the companies decided to use all their servers from the cloud providers’ data center.
- Private Cloud — When the companies decided to use all their servers on their own data center to replicate the cloud services e.g. offering self-service components.
- Hybrid Cloud — When the companies decided to use some of the servers in their own data center, and some of the servers in public cloud.
Part 2) Core Azure Services
This part contains the introduction to different services offering in Azure for each service category:
- Compute — Azure Virtual Machine, Container, Kubernetes Service
- Network — Azure Virtual Network, Load Balancer, VPN Gateway, Application Gateway and Content Delivery Network
- Internet of Things (IoT) — Azure IoT Hub, IoT Central
- Big Data & Analytics — Azure HDInsight, Data Lake Analytics, Databricks
- Artificial Intelligence — Azure ML, ML Studio
- Serverless Computing — Azure Function, Logic Apps
- Storage — Azure Blob Storage, Disk Storage, File Storage, Data Lake Storage
- Database — Azure SQL DB, SQL DW, CosmosDB
- Management tools — Azure CLI, Powershell, Portal, Advisor
- Azure Marketplace — Azure service for deploying ready to use services by Azure or the 3rd party. Such as a package to install and setup R Studio
Part 3) Security, Privacy, Compliance, and Trust in Azure
This part contains the security Azure provided for their services as well as Azure’s commitment in privacy and regulatory compliance.
Azure services for security in different areas:
- Network Security — Azure Firewall, DDoS Protection, and Network Security Group
- Authentication and Authorisation — Azure Activity Directory (AD)
- Application Security — Azure Key Vault, Information Protection, Advanced Threat Protection
- Resource Governance — Azure Policies & Initiatives, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Locks, Management Groups, Advisor
- Monitoring & Reporting — Azure Monitor, Service Health
- Privacy & Regulatory Compliance — Azure Government (for US governments), Germany (for EU’s GDPR regulation), Trust Center
Part 4) Azure Pricing and Support
This part contains the information about different types of Azure subscription, cost factors of Azure services, tools for cost calculation, and the support plans in Azure.
Azure subscription types:
- Free — New users will receive $200 credits to spend on any Azure products in the first 30 days. We will also receive free access to popular Azure products for the first 12 months, and the free access to free products forever. This type of subscript require credit card details, but nothing will be charged until we decide to upgrade to pay-as-you-go subscription.
- Pay-as-you-go (PAYG) — Charge monthly for the services used in the last billing period. This type is used by individuals and businesses.
- Enterprise Agreement — Enterprises can make an agreement with Azure which would allow discounted price for software license and Azure services.
- Student — Students will receive $100 credit to spend in the first 12 months. No credit card required for this subscription type, but the student email verification is required.
Cost Factors of Azure services:
- Resource Types — Different Azure products will have different pricing e.g. Azure VM cost will be based on the virtual machine size, operating system, usage hours, and storage size. The users can turn off virtual machine temporarily to save usage hours cost, but the storage cost will always incur.
- Subscription Types — Most users will pay the standard price, while the enterprise customers may have discounted or stable cost.
- Locations — For some resource types, the cost will vary based on the server locations. For example, Azure VM in Japan data center might cost more than in US data center.
- Inbound and Outbound traffic — Movement of data between different data center (availability zones) or regions might incur cost.
Tools for cost calculation for Azure
- TCO Calculator — The service to compare the cloud cost with the Total Cost of Ownership e.g. how much you need to spend if you are to build the same infrastructure in your own data center.
- Pricing Calculator — The website where the potential customers can plan their cost before moving to Azure cloud
- Azure Cost Management — Azure free service which shows how much have we spent in this billing period, and also provide the best practices to optimise the cost
- Azure Advisor — Azure free service which provides the recommendations in high availability, security, performance, and cost based on Azure products we are using
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
- SLA is the minimum time that Azure commit the service will be available to use. If the service is offline for longer time than SLA, Azure will provide credits for the customers.
- Azure offers 99.9% SLA on most Azure products
- There are some cases that the SLA can be increased. For example, Azure guarantees 99.99% SLA for the virtual machines that have more than one instance across more than one region.
Public Preview vs Private Preview features
- Most new features in Azure will be launched as private preview for limited users, then public preview for all the users
- After the feature has been thoroughly tested, it will be out of preview and become generally availability feature (GA).
- Azure provides Preview Portal for the users to test out new features for Azure portal. For other features that are not related to the portal, the users can access them from standard Azure portal.
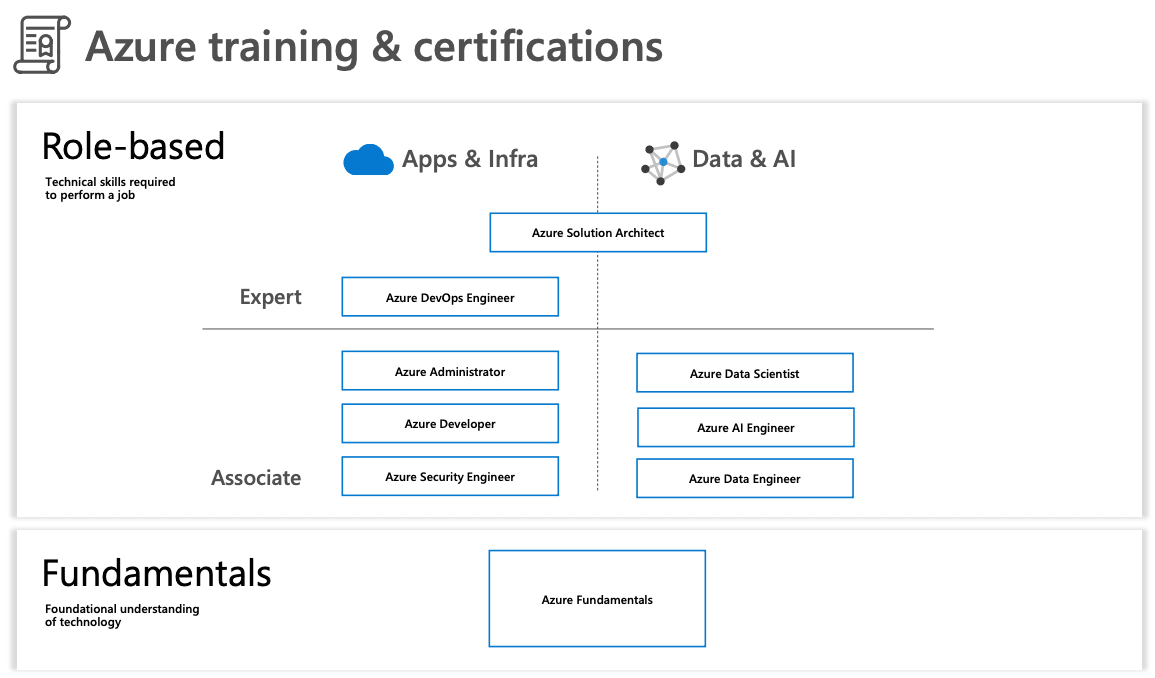
You are now ready for AZ-900!
What you will learn from the recommended courses listed above as well as the summary in this article will make you pass the exam with flying colors.
For the next step, the knowledge in AZ-900 exam is crucial for any Azure role-based certification in the future. Whether you would like to become Azure Administrator or Azure Data Engineer or any other roles, AZ-900 will be the great starting point for your career.
Wish everyone all the best for your exam!